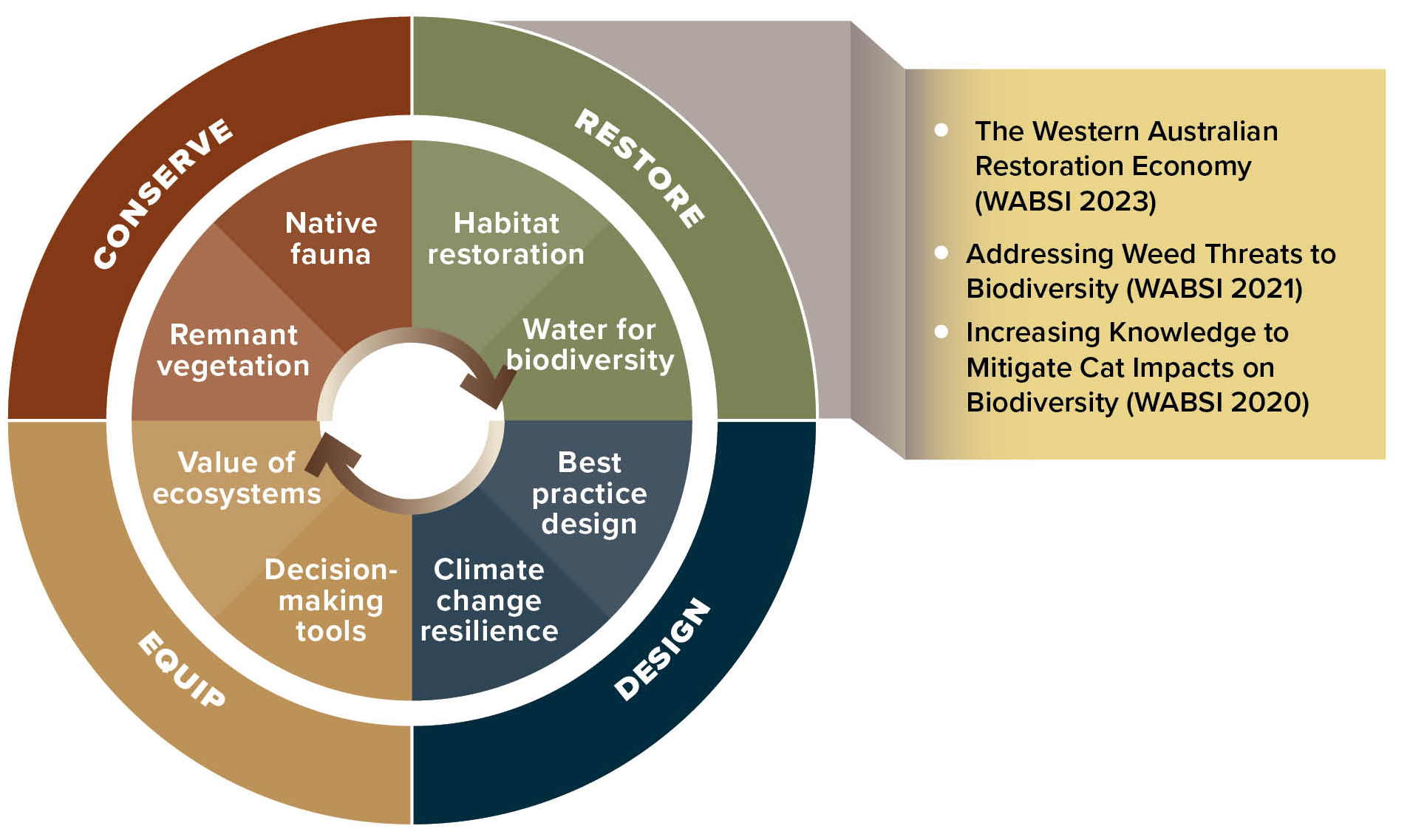



Prioritised research in key areas, shown above, can help address end user knowledge gaps in urban biodiversity resilience. (Click on each of the four themes to view key focus areas for research.)
Research program driven by the needs of end users – A collaborative approach, led by WABSI
WABSI undertook a series of workshops and stakeholder consultations with end users of biodiversity science and researchers, to identify critical knowledge gaps in urban biodiversity resilience. These consultations informed the development of a prioritised research framework for Western Australia.
Key themes and focus areas for research are shown in the diagram above. More information on each area is available by clicking on the link for each coloured area.
Download the research program publication:

Globally, urban development is causing major landscape changes and is frequently associated with loss of species richness and density, and increased homogenisation of ecological communities.
Compared to other cities nationally and internationally, the Perth urban landscape is relatively early in its development, however it is catching up fast and rapid urban growth has caused extensive biodiversity loss since British settlement nearly 200 years ago. Continuing development, especially at the fringes of the city, is the main catalyst for fragmentation of the landscape and the loss of native flora, fauna and ecosystem functions.
Western Australia is also experiencing the impacts of climate change. Perth’s climate is expected to become harsher under future climate projections. As Western Australia’s urban population density continues to rise, the environment faces greater climate risks, as do governments, industry and the wider community.
The issue requires a clear focus on collaborative opportunities for problem-solving, and tapping into existing resources, knowledge and expertise to apply best practice land management.
Collaboration between a broad group of stakeholders provides an opportunity to tackle the most pressing biodiversity challenges that are facing ecologists, policy makers, scientists, urban planners, developers and local governments.
WANT TO ENGAGE WITH US?
Submit a project abstract (aligned with the above priorities)